Blockchain Interoperability: A Prevailing Need in the Industry
LayerZero: Omnichain Interoperability Protocol
LayerZero: Omnichain Interoperability Protocol
With the arrival of Ethereum and smart contracts, the industry has seen exponential development in use cases within the ecosystem. However, the proliferation of DApps presents another challenge for developers inspired by the decentralization of blockchain technology: increasing fragmentation in a Web 3 world that depends on interconnectivity across applications.
Decentralized protocols have been adopted in spaces like finance, public records, certificates, and gaming.
Attracting the masses requires much effort with new technologies like the blockchain. And a key aspect demanded by the ‘masses’ is interoperability between the different blockchains that abound in the market.
A barrier to entry for many eager to venture into crypto is the complexity and intermediate knowledge they must possess to interact with a particular blockchain. Add to this the interaction with multiple protocols of different blockchains.
As the Web 3 narrative further develops, cross-chain interoperability is a mandate to ensure the sustainability of the industry, and it is precisely this philosophy that is driving the development of decentralized protocols with a cross-chain infrastructure to exchange and move assets freely between chains, especially in DeFi due to its promising trillion-dollar market.
Dune Analytics points out on its “Bridge Away” portal that more than $11.77B is locked up in bridges used to move assets between Ethereum and its competitors.
The above is just a sample of the enormous size, demonstrating the urgent need for solutions to move assets freely between chains.
However, this could change with the entry of LayerZero and its novel proposal to move assets between chains. But before we delve into it, let’s look at one of the most common problems in current solutions for trading assets across chains that LayerZero seeks to solve.
Common problems observed for the use of protocols interchain
The challenge of unifying blockchains and eliminating cumbersome transactional processes between cross-chain protocols has been one of the unresolved issues in the industry in recent years.
It is still difficult to find solutions that do not work in isolation in a chain or that resort to third parties to establish exchange bridges that have fragmented liquidity, high transaction costs, and a poor user experience with a high probability of unique failures that compromise the safety of the funds at stake.
The problem is mainly that to move assets between chains, solutions in the industry currently focus on two aspects:
The use of intermediate layers that execute the consensus to receive, validate and send the cross-chain message implies the execution of transactions, making it a single point of failure.
Running a light node on a chain. Despite being a highly effective solution at the security level to transmit messages between chains, its use is unlikely in most cases due to the cost of running a light node.
Under the above conditions, most solutions in the industry have opted for using intermediate layers between chains for sending messages.
This has caused a series of problems when multi-chain protocols are used to move assets of any kind:
1. Isolation of dApps to specific chains: Not all protocols for moving assets between chains are interoperable with all blockchain networks. Some are limited to specific blockchains, and the vast majority of solutions on the market for moving assets between chains are limited to specific layer 1 or 2 scaling solutions; EVM, non-EVM, etc.
This results in a severe problem of limited composability observed mainly in the decentralized finance sector, with wrapped, synthetic, and internal tokens of each protocol.
2. Using intermediaries as asset bridges can lead to common problems such as centralization and the risk of loss of funds due to the custody of third parties under a legacy trust system similar to a traditional financial system such as banks, contrary to the decentralized spirit of the blockchain.
Therefore, exposure to hacks and liquidity drainage in partially decentralized bridges with small validation systems, multi-sig, or vulnerable to attacks due to extreme trust in intermediate layers that are not completely decentralized are the order of the day.
3. The inefficiency and cost of wrapping assets cause issues in executing simple activities like borrowing on one chain against collateral located on a different chain is perhaps one of the biggest challenges seen when using cross-chain protocols or bridges to move cross-chain assets.
Although chain nodes can solve this point, they are ineffective due to the high computational load and money involved in the application.
Consequently, the user ends up with a cumbersome and tedious process of moving assets between chains using various interfaces and different transactions with different costs depending on the chain under which they are moving their assets.
Move assets between chains in a single transaction: LayerZero case
As we have mentioned before, one of the challenges of blockchain technology has been the simplicity of its use for users, especially when it comes to moving assets between chains.
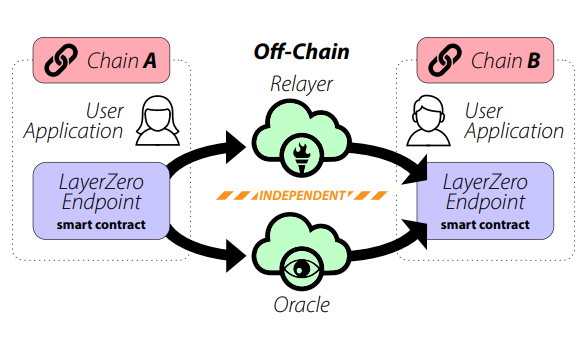
To solve this, LayerZero is breaking through with a simple but revolutionary approach based on a similar way of applying the concept of moving assets between chains using the traditional parameters of a blockchain transaction: block header and transaction proof.
To do this, it uses two independent entities, Oracle and Relayer, that act as cross-chain validators, thus considerably eliminating all the computational load and resources required to validate a transaction when moving assets between chains.
Instead, it uses a formalization of the communication primitive needed to allow cross-chain transactions, called valid delivery, while preserving blockchain security.
That is why LayerZero bills itself as the first trustless omnichain interoperability layer. It supports direct cross-chain messaging that allows assets to move freely at a low cost in a single transaction.
The key feature of the protocol is the ability to bundle transactions into one and pay for gas once, opening up a vast opportunity for dApp design that allows developers to:
Have wallets where the user does not need to know what chain they are on but can interact with any chain.
Create NFT markets where you can buy on any chain and move to any chain.
Unlock the DeFi space within each ecosystem without having to treat them all as entirely separate.
Benefits of the LayerZero protocol architecture
LayerZero is a configurable user application (UA) chain endpoint running an Ultra Light Node. To do this, as noted above, it uses the Oracle and Relayer to divide the responsibilities when establishing communication between chains during a blockchain transaction without the need to involve any intermediary chain.
The LayerZero protocol ensures that the transaction on the recipient’s chain matches a valid, committed transaction on the sender’s chain.
The benefits of LayerZero’s multi-chain architecture at the developer and user level:
1. Security: By dividing the responsibilities in executing and confirming a transaction with decentralized oracles such as independent Chainlink and Relayer, failure points are isolated and minimized to a part of the total assets at stake under an innovative risk model.
This differs from middle chain schemes for moving assets, where massive liquidity drain has been frequently observed in asset pool peers that use third-party validation to execute a transaction.
2. Simplicity in developing interfaces and codebase for cross-chain pairs: LayerZero produced a single powerful interface that can operate with any chain and pair to avoid the isolation of applications by chains or specific solutions such as Avalanche, Polygon, Ethereum.
3. Eliminate fragmented liquidity: The LayerZero protocol allows liquidity to be unified in all chains with a guaranteed purpose in the chain of origin. When a user transfers an asset from chain A to chain B, the user is guaranteed the asset on chain B, and LP providers receive fees on all incoming transactions to chain B, regardless of the chain of origin. This is disruptive and solves ‘The Bridging Trilemma’ as it is known in the blockchain industry: instant guaranteed finality, unified liquidity, and native assets.
The trifecta illustrated above makes it possible to avoid the reversal risks users face with current solutions, which result in a terrible user experience and, at the same time, unnecessary transaction costs.
4. Based on The Bridging Trilemma, LayerZero eliminates the need to use intermediate or synthetic tokens to provide liquidity. Native assets involve swapping a true/desired asset (USDC <> USDC) as opposed to swapping it into synthetic assets (USDC <> nUSD, anyUSDC, etc.).
This saves on unnecessary transaction fees for running multiple ‘bridges’ to move assets between different chains.
5. Composability: A single transaction from the origin chain without leaving the user interface enables powerful bridges to move assets in multi-chain applications, allowing the long-awaited composability in DeFi protocols.
6. LayerZero enables seamless deployment of AMMs regardless of chain, layer, or asset without modifying any existing code.
7. Unified governance: Run governance across multiple chains without swapping or moving all assets to another chain where governance lives.
8. User application layer: UAs can now own the entire cross-chain interaction and retain the user in their UI rather than linking out or needing the user to leave.
Promising future
Using a communication protocol such as the one proposed by LayerZero represents a turning point in the traditional way protocols have been used in the blockchain industry to move assets between chains.
The valid delivery-based communication primitive that allows the transfer of tokens between chains in a single click in the LayerZero protocol has been demonstrated in important use cases such as Stargate (Asset Bridge), its first application.
Stargate aims to facilitate token transfers between blockchains with a single transaction, avoiding the need for cumbersome steps like locking, minting, burning, and redeeming assets. This application managed to reach in April 2022 more than $4 billion in total value locked.
Another successful case has been the deployment of Ghostly Ghosts, a dynamic NFT collection deployed with the LayerZero protocol. The project positioned itself in Opensea as the Top NFT Project by sales volume last April, becoming the first NFT omnichain that activates functions such as cross-chain NFT arbitrage.
After only a few months online, LayerZero has the potential to help simplify cross-chain asset transactions in the industry, ultimately driving mass adoption of blockchain technology through frictionless cross-chain interoperability.