Deep Dive Into DIBA
Using Bitcoin, DIBA offers the opportunity to create, trade, and collect Unique Digital Assets (UDAs)
An Introduction to Bitcoin
At its inception, Bitcoin was designed to solve several issues brought on by dealing with financial intermediaries, such as high fees, long processing times, and the inevitable occurrence of fraudulent transactions. Consensus, transparency, and immutability were its core principles when it was created. Its rising popularity as a means of payment reflects shifting views on conventional forms of payment and established financial institutions (e.g., central governments and commercial banks).
Bitcoin was initially designed and released as a peer-to-peer payment method. However, its use cases are growing due to its increasing value and competition from other blockchains and cryptocurrencies.
DIBA - Digital Bitcoin Art and Assets
Before NFTs even existed, a revolution in how we think about freedom, money, ownership, and security was sparked by the invention of Bitcoin in 2009.
Using Bitcoin, DIBA offers the opportunity to create, trade, and collect Unique Digital Assets (UDAs).
The DIBA ecosystem allows art lovers to collect curated digital arts tied directly to Bitcoin's UTXOs (unspent Bitcoin transaction outputs). It is the first Bitcoin digital marketplace to use RGB Smart Contract Protocol and Lightning Network (BP/LNP) to exchange UDAs.
The difference between NFTs and UDAs
When something is described as non-fungible, it has a unique quality that makes it irreplaceable.
UDA stands for Unique Digital Asset, which could be used similarly to NFT. DIBA uses the term UDA to refer to an asset attached to a Bitcoin UTXO (unspent transaction output), which can simply be a piece of Bitcoin. A Unique Digital Asset is created from an RGB Smart Contract Protocol tying an asset to a Bitcoin UTXO. The owner of the Bitcoin UXTO within the UDA is the owner of the UDA.
Many other benefits result from UDAs inheriting all of Bitcoin's qualities, such as lower fees, the enduring value of art, and security supported by the most robust blockchain. The Bitcoin and digital art communities have never seen anything like this structure before.
Lightning Network
By implementing scaling solutions, which aim to increase the system's scalability and functionality, it is possible to build on the Bitcoin blockchain. Scaling solutions, also known as L2s, abstract some functions from the base layer but only rely on them for security and immutability.
The most well-known method for scaling Bitcoin-based applications is Lightning Network. Small transactions don't necessarily need to be recorded on the blockchain, the central tenet of the Lightning Network's design.
By enabling off-chain transactions, Lightning increases system throughput. The final state of these transactions is documented on the blockchain to guarantee security and immutability.
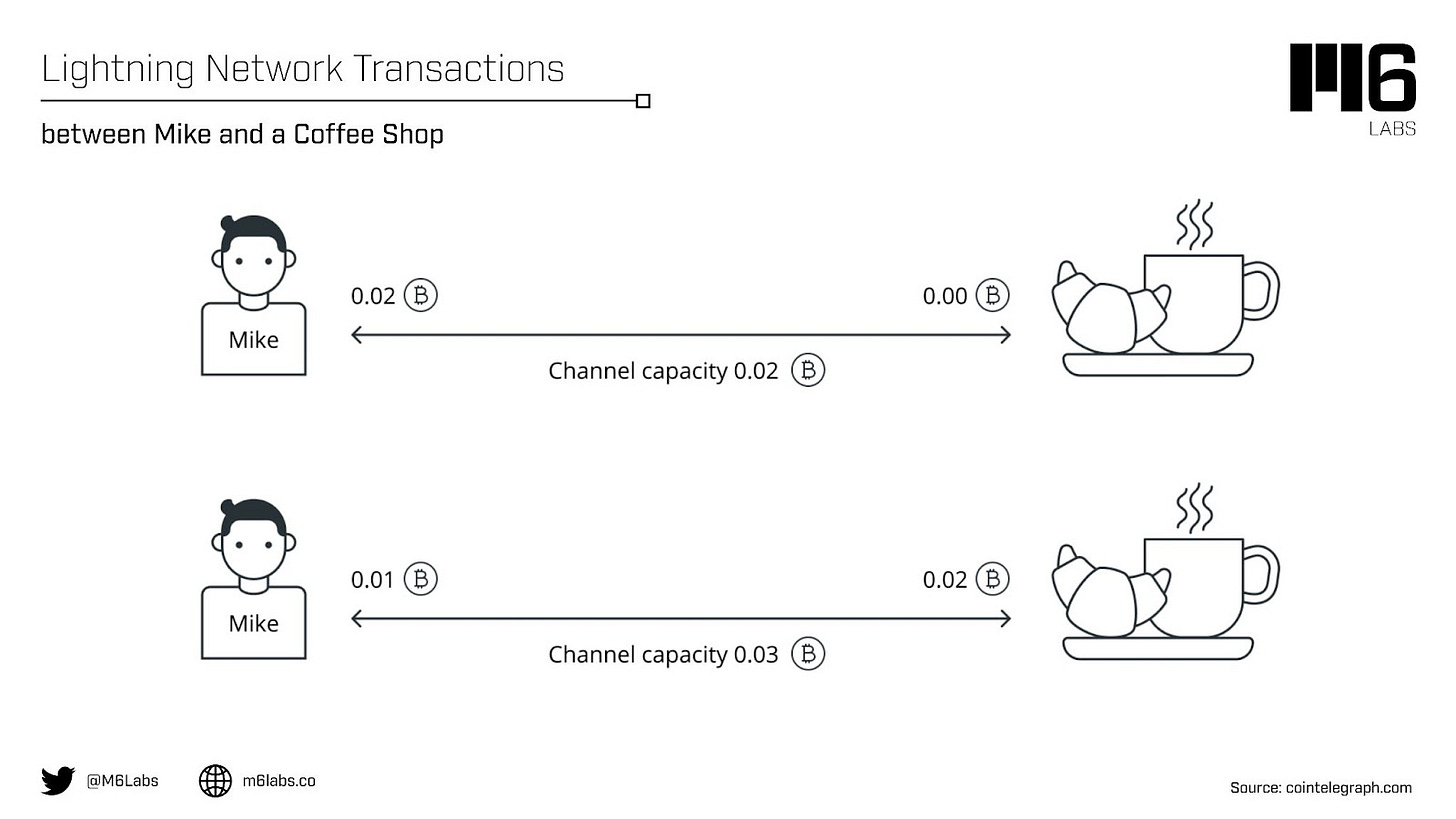
One of the most popular examples of how a Lighting Network works:
Mike frequently visits a neighborhood coffee shop and prefers to pay with Bitcoin. He could decide to make a small transaction for each coffee cup, but the transaction could take more than an hour to validate due to scalability issues with Bitcoin. Even though Mike only makes a small transaction, Mike must also pay the high fees associated with the Bitcoin network. Traditional payment methods, like a card, are effective for small transactions because they have the infrastructure to handle more than 24,000 TPS, thanks to businesses like Visa. In contrast, Bitcoin can validate seven TPS on an average day.
Mike can establish a payment channel with the coffee shop using the Lightning Network. Each purchase of coffee is tracked through that channel, and the shop still gets paid. The transaction is quick, low-cost, and may even be free. Mike can then decide whether to close the channel or reopen it after the Bitcoin that initiated it has been used. Once closed, a channel's transactions are added to the main Bitcoin blockchain.
Between the two parties, the Lightning Network establishes a smart contract. The terms of the agreement are written into the contract at creation and cannot be changed. As contracts are initially made with predetermined requirements that all parties agree with, smart contract code also ensures that contract fulfillment is automatic. When those conditions are satisfied, such as when a customer pays the appropriate amount for a coffee, the contract automatically completes without needing a third party. Once a transaction has been validated in a payment channel, the Lightning Network encrypts it. Nobody can see the transactions that made up the value transfer; they are all visible together.
Pros of Lightning Network
1. Speed (Transactions per Second)
2. Privacy
3. Transaction Costs
Cons of Lightning Network
1. Erosion Of Incentives (certain assets lose value over time)
2. Transaction Risks And Security
3. Reliance On Bitcoin
RGB: scalable & private smart contracts for Bitcoin & Lightning
Another piece of DIBAs technology is RGB protocol which promises to enable complex smart contracts that operate on top of Bitcoin and Lightning.
RGB is a collection of open-source protocols that enables secure, scalable execution of complex smart contracts. Each smart contract is just a group of contract participants who can communicate with one another via various communication channels; it is not a specific network (like Bitcoin or Lightning). RGB maintains the smart contract code and data off-chain to scale and uses the Bitcoin blockchain as a layer of state commitment. The evolution of the smart contract is determined by an off-chain scheme that uses Bitcoin transactions (and Script) as an ownership control system. It's important to remember that all validation occurs on the client side.
Simply put, RGB is a system that, unlike traditional methods that use a blockchain, enables users to audit, execute, and independently verify smart contracts at any time without incurring additional costs. Although Ethereum invented sophisticated smart contract systems, it never attained the promised scalability and eventually required users to pay significant amounts of gas for each operation. As a result, Ethereum was only viable for users who were happy to pay for those operations.
RGB’s main properties
Confidentiality
Safety
Scalability
No Bitcoin time chain congestion: transactions keep only homomorphic commitments which require no additional storage
Future-ready without hard forks
Higher censorship resistance than in Bitcoin: miners do not see that something is going on with assets in transactions


On DIBA, how are Bitcoin UDAs created and stored?
Any assets, such as the original photos and thumbnails, are uploaded to the Arweave permaweb when created. These go along with a cryptographic hash that, when combined with a digital signature, can be used to confirm the validity of the assets. UDAs are transferred through an RGB Smart Contract, which can be used to conduct transactions in BitMask, a wallet developed by DIBA.
Bitmask is a Chrome extension wallet created by DIBA that supports stablecoins and UDAs.
BitMask is built for speed and security using Rust and BDK, compiled into WebAssembly. This wallet supports Bitcoin transactions in addition to RGB assets and uses Taproot transactions by default. Lightning support for assets and sats is planned for later in the year.
DIBA Marketplace
DIBA’s Open Marketplace was open for beta testing beginning in April 2022. DIBA BETA is available on Bitcoin testnet. Submissions to be on DIBA's Curated Marketplace are open now. You can submit to be an Artist or a Curator on the Curated Marketplace.
DIBA's first Curated Drop will take place this year!
DIBA Events and Competitions
This year, DIBA was present at the world's largest, most reputable Bitcoin event through talks, digital art, and DIBA’s first-ever official afterparty.
The Bitcoin Conference Pitch Competition could measure DIBAs development within the context of the Bitcoin Miami Conferences, as DIBA was honored as one of the Top 10 Finalists at the competition in 2021.
DIBA attended the conference in Miami again ten months later as an official partner and a platform with a featured exhibition inside the Bitcoin Conference.
DIBA Team
DIBA's strong team built a new digital art and asset marketplace on Bitcoin from America to the UK, Spain, and Indonesia.
FOUNDER & CEO - Gideon Nweze founded DIBA to help millions of people understand, own, and collect non-custodial digital assets issued on Bitcoin. He believes in the ability of technology to distribute wealth and access to resources for all people.
HEAD OF ENGINEERING - Jose Robles joined the DIBA team after meeting the founder, Gideon, while collaborating on RGB open-source projects. He is enthusiastic about the future of NFTs and is excited to make digital assets on Bitcoin through Bitmask and DIBA a reality.
MARKETING & BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT - Anastasiia Ilicheva is the Co-Founder and COO of The Babylon Project Hackathons by World Blockchain Hackathon. With her strong interest and experience in blockchain, Anastasiia joined the DIBA team to onboard more people into the Bitcoin and NFT communities.
DIRECTOR OF ENGINEERING - Hunter Trujillo has a prior background in Web 3 as a former JS developer and has been a web developer since 2009. Once a principal engineer for a Fortune 500 company, Hunter co-founded several blockchain startups, fulfilling the CTO role, where he gained experience in engineering management.
UI/UX DESIGNER - Tasha Amanda, DIBA sparked Tasha’s curiosity because of the diverse team and her interest in crypto. She enjoys interacting with people from all over the world and learning more about Bitcoin. New to the NFT space, Tasha brings her passion for the creative field into developing the DIBA platform, built to uplift the artistic community.
SOFTWARE ENGINEER - Trevor O’Farrell is a self-taught Web Developer who has worked on many digital projects. While building a virtual art gallery for a crypto hackathon, Trevor came across DIBA and joined the team.
DIBA's Upgrade
The newest version of BitMask is something DIBA Global is proud to share. DIBAs first release in more than two months is BitMask 0.4.
Highlights of the BitMask 0.4 Update:
Taproot support
Deprecation of SegWit addresses
Asset import by RGB genesis now works, but asset import by RGB ID does not
Integration of UDAs from the DIBA marketplace
What’s next?
DIBA's team is currently working with Dr. Maxim Orlovsky and the RGB community to get WASM support to deprecate that portion of DIBA's infrastructure sometime next year.
Additionally, they are developing a storage format called Carbonado so that wallet data can be reliably persisted in a compressed, encrypted, error-corrected, and remotely-verifiable file format.
They are also working on future UI/UX improvements for handling mnemonic seed phrases. It will use keys generated by your wallet to implement authenticated encryption.
The beauty of Bitcoin lies in its rarity and longevity, and DIBA wants to provide users with tools they can use for a very long time.
The Founder Gideon added the following quote regarding DIBAs mission:
At DIBA, we are a product focused company.
We believe that it is possible to build hard things and bring a very high level of simplicity to complex technologies that has the capacity to move humankind in the right direction.
We are helping realize the collective dream of humanity through art and technology
And remember…
Stay connected with DIBA for the latest updates:
DIBA website - https://diba.io/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/trydiba
Discord - https://discord.com/invite/KBFHJ4knXe
Instagram - https://www.instagram.com/trydiba/
Telegram - https://t.me/tryDIBA
Subscribe to receive our daily brief, extended weekly newsletter, and in-house research content!
Please Share, Leave Feedback, and Follow Us on Twitter, Telegram, and LinkedIn to stay connected with us.